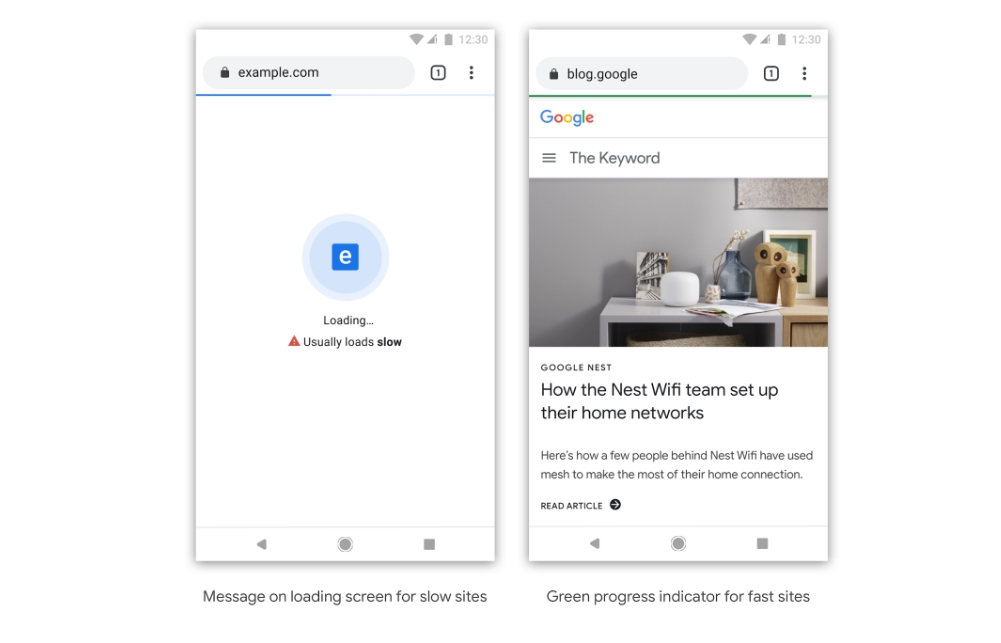
During the summit, Google proposed that a slow website be flagged down may get a “Loading” warning sign, accompanied by a text that reads “Usually loads slow”. On the other hand, fast websites may have a green content progress indicator bar to indicate that its loading speed is on par.
Mind you, these methods of identification are still not finalised, and Google is still working on other methods to “speed-badge” a site. On that note, Google says that there’s also the possibility of using a site’s load latency as a form of measurement. Additionally, that form of measurement could also be used to identify if a site is going to run slow. Either when using a certain device or because of fluctuating network conditions. For web optimisation, Google also suggested using its site performance resources including PageSpeed Insights, the online tool for optimization suggestions and Lighthouse, a personalised advice tool. Additionally, Google has provided web.dev/fast as a learning platform to optimise your website.
Previously, Google announced that Chrome would block advertisements that were using up too many resources to speed up website loading times. In regards to the speed-badging, Google did not mention when the update will actually be implemented. (Source: Chromium via Engadget, Techspot, TechCrunch)